
- KVM VS VMWARE VS VIRTUALBOX SOFTWARE CREATES AN
- KVM VS VMWARE VS VIRTUALBOX FREE VERSION THAT
- KVM VS VMWARE VS VIRTUALBOX FULL VIRTUALIZATION SOLUTION
Kvm Vs Vmware Vs Virtualbox Full Virtualization Solution
Kvm Vs Vmware Vs Virtualbox Software Creates An
Each virtual machine runs its own operating system (OS) and behaves like an independent computer, even though it is running on a portion of the actual underlying computer hardware.As you can imagine, virtualization enables more efficient utilization of computer hardware and enables a greater return on an organization’s hardware investment. It tightly integrates the KVM hypervisor and Linux Containers (.Simply put, VMware (link resides outside IBM) develops virtualization software.Virtualization software creates an abstraction layer over computer hardware that allows the hardware elements of a single computer— processors, memory, storage, and more— to be divided into multiple virtual computers, commonly called virtual machines (VMs). What is VMware?KVM vs VirtualBox: What are the differences Developers describe KVM as 'Kernel-based Virtual Machine is a full virtualization solution for Linux'.KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V).Proxmox VE is a complete, open-source server management platform for enterprise virtualization. VMware Workstation Pro in 2021 by cost, reviews, features, integrations, deployment, target market, support options, trial offers, training options, years in business, region, and more using the chart below.Learn more about VMware, virtualization software, virtual machines, and how they are all a crucial part of many enterprises' IT infrastructures. Migrating to a KVM-based virtualization platform means being able to inspect, modify, and enhance the source code. KVM is an open source virtualization technology that changes the Linux kernel into a hypervisor that can be used for virtualization and is an alternative to proprietary virtualization technologies, such as those offered by VMware.
You can configure virtual machine settings using the vSphere Client, which is a command-line interface for VM management. An operating system (OS) running in a VM is called a guest OS.Each VM includes a configuration file that stores the VM’s settings, a virtual disk file that is a software version of a hard drive, and a log file that keeps track of the VM’s activities, including system failures, hardware changes, migrations of virtual machines from one host to another, and the VM’s status.VMware offers various tools for managing these files. A VM is a software-based representation of a physical computer. Virtual machines (VMs)A virtual machine (VM) is the base unit of VMware virtualization.
Industry support: VMware is the foremost provider of virtualization services, with over 500,000 customers. Fewer physical servers require less space in your data center and less energy to power and cool. More efficient use of energy and space: VMware lets you run more applications using fewer physical servers. With VMware, you can run each application in its own OS on the same physical server and make better use of the physical server’s available CPU power,
VMware ESXVMware's ESXi data center-focused hypervisor (link resides outside IBM) is a Type 1 or "bare metal" hypervisor, replacing the primary operating system that would interact with a computer’s physical components. Should one guest OS suffer an application crash, become unstable, or become infected with malware, it won't affect the performance or operation of other operating systems running on the host.“ Hypervisors: A Complete Guide” gives a full overview of what hypervisors are and how they work. The guest OS requests resources from the hypervisor.The hypervisor separates each guest OS so each can run without interference from the others. A hypervisor is a thin layer of software that interacts with the underlying resources of a physical computer (called the host) and allocates those resources to other operating systems (known as guests). VMware hypervisorVMware virtualizes physical computers using its core hypervisor product.
When activated, it installs itself alongside the Windows OS in a root partition, which gives Windows privileged access to the underlying hardware. Hyper-V must run with the Windows OS. Hyper-V works differently to ESXi, using partitions to manage its VMs. Like VMware's ESXi, Hyper-V is a Type 1 hypervisor that interacts with the underlying physical computing and memory resources. Hyper-V: Microsoft's Hyper-V is a hypervisor product that allows you to run multiple operating systems on the same server or client computer. VMware has discontinued ESX.VMware’s ESXi competes with several other Type 1 hypervisors:
KVM's big advantage over VMware ESXi is that it is an open source product, making its code base transparent. KVM: Both VMware ESXi and KVM are hypervisors, but KVM is part of the Linux kernel (the heart of the OS). Citrix’s application and desktop virtualization products compete with VMware’s Horizon virtual desktop integration product. Its main hypervisor offering is the Citrix Hypervisor (known as XenServer), which competes with VMware vSphere. Citrix: Citrix offers application and desktop virtualization products and has a long track record in the virtual desktop integration market. Hyper-V also ships with Windows 10 clients, competing with VMware's Type 2 Workstation hypervisors.
ESXi supports a wide range of Linux guest operating systems including Ubuntu, Debian, and FreeBSD. When VMware released ESXi, it replaced the Linux kernel with its own. The early version of its hypervisor, called ESX, included a Linux kernel (the central part of an OS that manages the computer hardware). You can also buy Red Hat Virtualization, which provides a suite of management tools for virtual servers built on KVM.VMware relied on Linux during its early history. As with many open source projects, they might need extra configuration work.
Kvm Vs Vmware Vs Virtualbox Free Version That
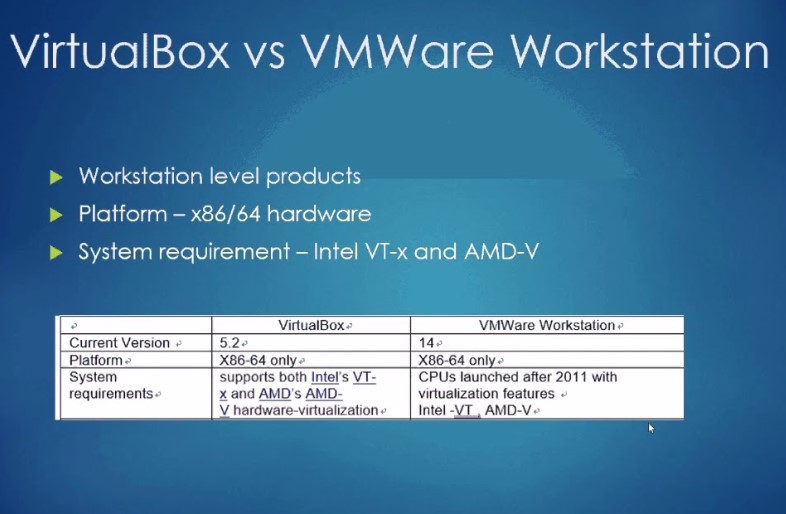
Workstation Pro (link resides outside IBM) supports multiple guest operating systems and integrates with VMware's enterprise virtualization management tools.There’s only one thing better than having a second OS on your desktop computer: having a second OS that can exchange data with the first. Workstation Player (link resides outside IBM) is a free version that supports a single guest OS. Unlike a Type 1 hypervisor, which replaces the underlying OS altogether, a Type 2 hypervisor runs as an application on the desktop OS and lets desktop users run a second OS atop their main (host) OS. What is VMware Workstation?VMware Workstation includes Type 2 hypervisors. This section covers some of that software and how it works.
You then access the CD-ROM image from within the guest OS and run the installer.See the full installation instructions in the VMware Tools documentation (link resides outside IBM).VMware’s Type 2 hypervisors compete with others on the market, including the following: VMWare Workstation then mounts a virtual CD-ROM drive in the guest OS that contains the VMware Tools installer. You can use it to drag and drop files and to cut and paste between the two operating systems.To install VMware Tools, click VM and then Install VMware Tool s from the VMware Workstation menu. It enables the guest OS running within the Type 2 hypervisor to work better with the host OS.The benefits of installing VMware Tools include faster graphics performance and support for shared folders between the guest and host OS. It is a crucial part of any VMware Workstation environment.
It competes with VMware Fusion. Parallels: Parallels is a Type 2 hypervisor dedicated to running guest operating systems on the macOS platform. VMware's products offer better support for 3D graphics, while VirtualBox supports more virtual disk images, which are files that contain virtual machine data. VirtualBox supports Linux, Windows, Solaris, and FreeBSD as host operating systems.Each product has its strengths and relative weaknesses in different areas. It is a free, open source product that allows you to install and use another OS on top of the one already on your desktop or laptop.You can install VMware's products on Linux and Windows.
VDI virtualizes desktop operating systems on a server.VDI offers centralized desktop management, letting you configure and troubleshoot desktop operating systems without remote access or on-site visits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
